SDS
SDS是Redis中存储string的底层数据结构,定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| /* Note: sdshdr5 is never used, we just access the flags byte directly.
* However is here to document the layout of type 5 SDS strings. */
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, and 5 msb of string length */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
|
- 对比c语言字符串,SDS实现为动态字符数组,可以高效的进行strlen,append等操作,并且是二进制安全的
- Redis用不同类型的结构体(主要区别在于
len和alloc字段)存储不同大小的string,使用attribute ((packed))来实现紧凑的内存布局,从而节省内存消耗。
skiplist
skiplist(跳表)是zset的底层数据结构之一,
跳表实现为多层链表结构,其顶层链表节点比底层少,可以起到索引的作用:
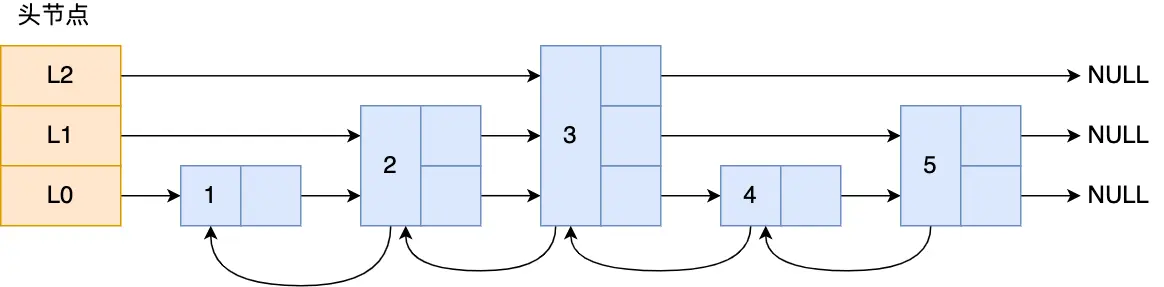 其结构定义如下:
其结构定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| // 跳表节点
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
sds ele;//元素值
double score;//分值
struct zskiplistNode *backward;//前驱节点
struct zskiplistLevel {
struct zskiplistNode *forward;//后继节点
unsigned long span;//与后继节点间的跨度
} level[];
} zskiplistNode;
// 跳表
typedef struct zskiplist {
struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;
unsigned long length;
int level;//层级
} zskiplist;
// 跳表实现的zset 结构
typedef struct zset {
dict *dict;
zskiplist *zsl;
} zset;
|
查找
redis 中的跳表支持两种类型的查找:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| /* Find the first node that is contained in the specified range.
* Returns NULL when no element is contained in the range. */
zskiplistNode *zslFirstInRange(zskiplist *zsl, zrangespec *range) {
zskiplistNode *x;
int i;
/* If everything is out of range, return early. */
if (!zslIsInRange(zsl,range)) return NULL;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
/* Go forward while *OUT* of range. */
while (x->level[i].forward &&
!zslValueGteMin(x->level[i].forward->score,range))
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
/* This is an inner range, so the next node cannot be NULL. */
x = x->level[0].forward;
serverAssert(x != NULL);
/* Check if score <= max. */
if (!zslValueLteMax(x->score,range)) return NULL;
return x;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| /* Finds an element by its rank. The rank argument needs to be 1-based. */
zskiplistNode* zslGetElementByRank(zskiplist *zsl, unsigned long rank) {
zskiplistNode *x;
unsigned long traversed = 0;//当前节点的编号
int i;
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->level[i].forward && (traversed + x->level[i].span) <= rank)
{
traversed += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
if (traversed == rank) {
return x;
}
}
return NULL;
}
|
这两种查找过程是类似的:
- 从顶层开始查找
- 找到该层最后一个小于目标值的节点
- 进入下一层查找或退出
- 判断退出时的节点的下一个节点值是否等于目标值
由于底层是双链表结构,所以可以很好的支持范围查找,只需要根据找到的起始值进行前(后)向遍历即可。
插入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| zskiplistNode *zslInsert(zskiplist *zsl, double score, sds ele) {
zskiplistNode *update[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL], *x;
unsigned int rank[ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL];
int i, level;
serverAssert(!isnan(score));
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
/* store rank that is crossed to reach the insert position */
rank[i] = i == (zsl->level-1) ? 0 : rank[i+1];
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0)))
{
rank[i] += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
update[i] = x;
}
// 获得一个随机层数
level = zslRandomLevel();
if (level > zsl->level) {
for (i = zsl->level; i < level; i++) {
rank[i] = 0;
update[i] = zsl->header;
update[i]->level[i].span = zsl->length;
}
zsl->level = level;//更新跳表层数
}
// 创建新节点
x = zslCreateNode(level,score,ele);
// 更新新节点的每一层指针关系
for (i = 0; i < level; i++) {
x->level[i].forward = update[i]->level[i].forward;
update[i]->level[i].forward = x;
/* update span covered by update[i] as x is inserted here */
x->level[i].span = update[i]->level[i].span - (rank[0] - rank[i]);
update[i]->level[i].span = (rank[0] - rank[i]) + 1;
}
/* increment span for untouched levels */
for (i = level; i < zsl->level; i++) {
update[i]->level[i].span++;
}
// 更新新节点的backward指针
x->backward = (update[0] == zsl->header) ? NULL : update[0];
if (x->level[0].forward)
x->level[0].forward->backward = x;
else
zsl->tail = x;
zsl->length++;//更新跳表长度
return x;
}
|
插入的过程:
- 找到每层的插入位置(待插入节点的前驱节点)记录到update数组中
- 初始化待插入的节点
- 将新节点插入到每一层
这个过程中有几个细节的点:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| int zslRandomLevel(void) {
int level = 1;
while ((random()&0xFFFF) < (ZSKIPLIST_P * 0xFFFF))
level += 1;
return (level<ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL) ? level : ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL;
}//其中 ZSKIPLIST_P=0.25 ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL=32
|
- span值的更新,span值用来支持编号查询
- backward指针的更新,仅在底层
删除
删除的过程类似于新增的过程,需要先找到update数组和待删除的节点x,
具体删除节点的代码如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| void zslDeleteNode(zskiplist *zsl, zskiplistNode *x, zskiplistNode **update) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < zsl->level; i++) {
if (update[i]->level[i].forward == x) {
update[i]->level[i].span += x->level[i].span - 1;//更新span
update[i]->level[i].forward = x->level[i].forward;//更新forward指针
} else {
update[i]->level[i].span -= 1;//更新span
}
}
if (x->level[0].forward) {
x->level[0].forward->backward = x->backward;//更新backward指针
} else {
zsl->tail = x->backward;
}
// 更新跳表层数
while(zsl->level > 1 && zsl->header->level[zsl->level-1].forward == NULL)
zsl->level--;
zsl->length--;//更新跳表长度
}
|
 其结构定义如下:
其结构定义如下: